I used Sun Virtual Box before. I’ve just installed Oracle Virtual Box on my old Vista to try Fedora 14. All I had to do was to download x86_64 Network Install CD and go through a minimal installation.
The first hiccup was I needed to eject CD (ISO image) of the virtual machine (VM) when the installer required to reboot the system. Then, I took a snapshot of this minimalistic system, about 1.1GB.
The second hiccup was the network adapter. I could not connect to the Internet. The VM was set up to use NAT by default. I had to change it to bridged. After restarting the VM, I had to run:
/etc/init.d/network restart
And I could connect using putty from my Vista environment.
I prefer to run Subversion with Apache HTTP Server. So;
yum install httpd
I’m not a vi fan, so I had to install nano to edit configuration files easily:
yum install nano
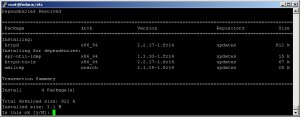
To install Subversion on Fedora, they say you can run:
yum install subversion
Yum checks dependencies and you have to accept to install them as well.
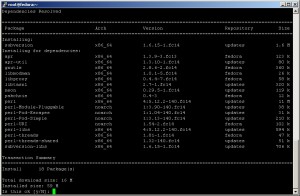
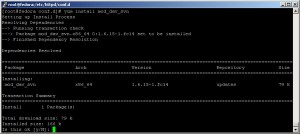
Also, to glue the two server (SVN and Apache HTTP) install mod_dav_svn:
yum install mod_dav_svn
I’m sure you will find SVN easy to use, and find many sites explaining how to creating a new repository (or repositories, another debate).
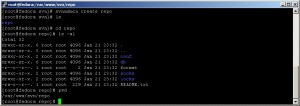
cd /the-path-to-svn-repository
#such as /var/www/svn
svnadmin create repo
svn mkdir file:///var/www/svn/repo/project1 -m "Creating project1"
There are many ways to create a layout but I choose to create a directory per project with sub-directories of trunk, branches and tags.
svn mkdir file:///var/www/svn/repo/project1 -m "Creating project1"
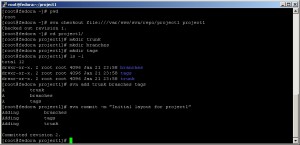
Inside your home directory checkout project1 (still empty directory):
cd ~
svn checkout file:///var/www/svn/repo/project1 project1
cd project1
mkdir trunk
mkdir branches
mkdir tags
svn add trunk branches tags
svn commit -m "Initial layout for project1"
Now, let’s share our SVN repository with our team members.
cd /etc/httpd/conf.d/
nano subversion.conf
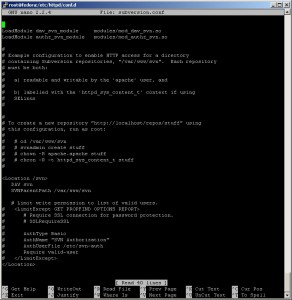
For me, main point is to be able to serve SVN repository, so, just define the location and change ownership/permissions on directory for SVN repository.
cd /var/www/svn
chown -R apache.apache repo
The system is ready to be used by team members remotely using SVN clients such as TortoiseSVN. On the command line, it is as easy as:
svn co http://localhost/svn/repo/project1 project1
Later, I may write about Subclipse which adds SVN integration to my favourite PHP IDE, Eclipse PDT.
Happy coding!